Understanding the Differences: ICE, BEV, MHEV, and Other Vehicle Types
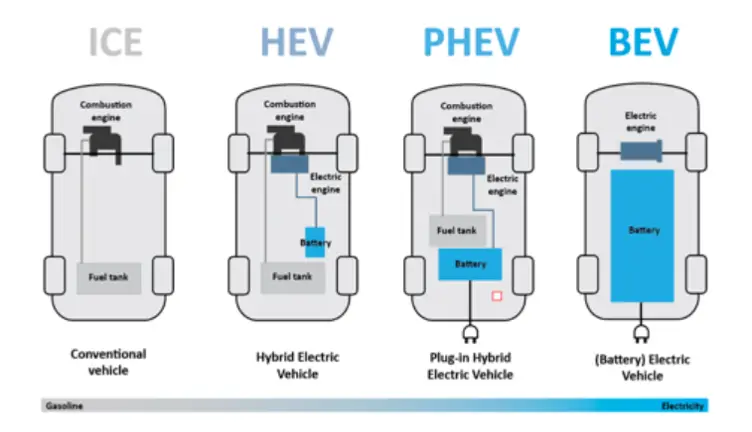
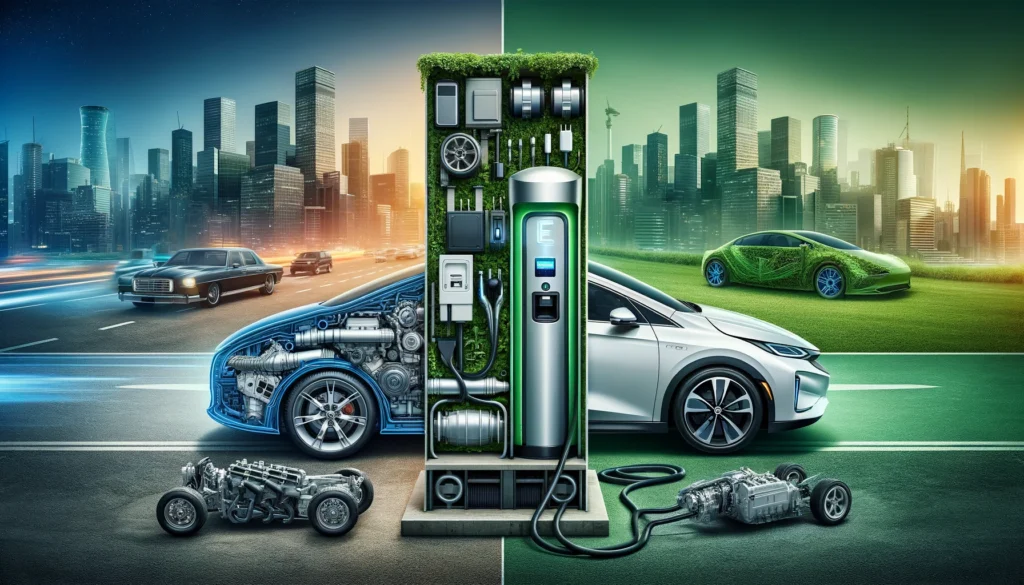
In today’s rapidly evolving automotive landscape, it’s crucial to understand the differences between various vehicle types. From traditional Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) vehicles to Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) and Mild Hybrid Electric Vehicles (MHEVs), each type offers distinct advantages and disadvantages. This guide will help you navigate these differences, shedding light on how they impact performance, efficiency, and sustainability.
Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) Vehicles
What are ICE Vehicles?
ICE vehicles are powered by internal combustion engines, which burn fuel (typically gasoline or diesel) to create mechanical energy. This has been the dominant vehicle technology for over a century.
Pros:
- Established Infrastructure: Fueling stations are widespread and convenient.
- Proven Technology: Mature and reliable, with a long history of development.
- Lower Initial Cost: Generally cheaper to purchase than electric vehicles.
Cons:
- Environmental Impact: High emissions contribute to pollution and climate change.
- Fuel Dependency: Dependent on fossil fuels, which are finite and subject to price volatility.
- Maintenance: More complex mechanics lead to higher maintenance costs over time.
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)
What are BEVs?
BEVs are fully electric vehicles powered by batteries, which store electrical energy and drive electric motors. They have no internal combustion engine and produce zero tailpipe emissions.
Pros:
- Environmental Benefits: Zero emissions at the point of use.
- Efficiency: Electric motors are more efficient than combustion engines.
- Lower Operating Costs: Electricity is generally cheaper than gasoline, and maintenance is simpler due to fewer moving parts.
Cons:
- Range Anxiety: Limited driving range compared to gasoline vehicles, though this is improving.
- Charging Infrastructure: Still developing, though rapidly expanding.
- Higher Upfront Cost: Typically more expensive to buy, though incentives and falling battery prices are mitigating this.
Mild Hybrid Electric Vehicles (MHEVs)
What are MHEVs?
MHEVs combine a traditional ICE with a small electric motor that assists the engine. The electric motor cannot power the car on its own but provides additional power during acceleration and can recover energy during braking.
Pros:
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: Electric assistance reduces fuel consumption.
- Lower Emissions: Reduced emissions compared to traditional ICE vehicles.
- No Range Anxiety: No need for charging infrastructure as the vehicle relies on regenerative braking and the ICE for energy.
Cons:
- Complexity: More complex than a traditional ICE vehicle, potentially leading to higher maintenance costs.
- Less Efficient than Full Hybrids or BEVs: The electric motor provides only limited assistance.
Other Vehicle Types
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs):
PHEVs have both an internal combustion engine and a larger battery pack than MHEVs, allowing them to drive a significant distance on electric power alone before the engine kicks in.
- Pros: Greater electric-only range than MHEVs, flexibility of ICE for long trips, lower emissions.
- Cons: Higher cost, need for charging infrastructure to maximize benefits.
Full Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs):
HEVs combine a gasoline engine with an electric motor and battery, allowing for seamless switching between or combination of power sources.
- Pros: Improved fuel efficiency and lower emissions, no need for external charging.
- Cons: More complex system, which can lead to higher maintenance costs.
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles (FCVs):
FCVs use hydrogen gas and oxygen from the air to produce electricity, which powers an electric motor.
- Pros: Zero emissions, fast refueling, long range.
- Cons: Limited refueling infrastructure, high production costs, and the need for sustainable hydrogen production.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between ICE, BEV, MHEV, and other vehicle types is essential for making informed decisions about your next vehicle purchase. Each type offers unique benefits and drawbacks, influenced by factors such as environmental impact, operating costs, and infrastructure availability. Whether you prioritize sustainability, cost-efficiency, or convenience, there’s a vehicle type that can meet your needs. By staying informed, you can choose the best option for your lifestyle and contribute to a more sustainable future.







